AI in Warehouse Management – Challenges, Benefits, Costs
Table of Contents
Subscribe To Our Newsletter

In a Nutshell:
- Warehouses are under pressure from labor shortages, rising costs & real-time order demands.
- Traditional systems can’t keep up – AI brings predictive, responsive & automated solutions.
- AI benefits include sharper forecasting, faster picking, safer workplaces, better layouts & smoother decision-making.
- Implementation costs vary- $50K+ for small warehouses to millions for large, fully automated facilities.
- ROI arrives in 18 to24 months, driven by reduced errors, lower labor costs & faster order fulfilment.
- By 2030, AI in logistics and warehouses may cross $35 to 50B, making adoption urgent for competitiveness.
Warehouses used to be sleepy backrooms of commerce. Aisles of stacked boxes, forklifts humming & managers relying on clipboards or clunky spreadsheets. Fast forward to the e-commerce era and things looks different-way more chaotic. Orders pour in around the clock, delivery windows shrink to hours & customers refresh tracking pages like they’re watching a game.
And here’s the kicker-traditional warehouse management systems were never built for this speed. They’re fine for yesterday’s supply chains, but today? They buckle under real-time demands. This is where AI in warehouse management steps in. Artificial intelligence in warehouse operations isn’t just another software upgrade. It’s a fundamental shift in how warehouses think, move & respond.
In this blog, we’ll unpack the messy challenges warehouses face, the practical benefits of AI (not the sugar-coated ones) & yes-the costs you should expect. Because let’s be real-deploying AI isn’t free, but running a warehouse without it might cost you a lot more.
The State of Modern Warehousing
Walk into a modern warehouse and you’ll see the problem. Rows of pallets stacked to the ceiling, pickers hustling to meet impossible targets & managers trying to keep up with spreadsheets that never quite match reality. Add labor shortages, seasonal order spikes & customers who expect delivery in hours, not days. It’s a system stretched to its limits.
Most warehouses still rely on older systems stitched together with minimal integration. Inventory updates lag. Space goes underused. Small mistakes snowball into costly delays. The pace of commerce today leaves no room for that kind of drag.
This is where warehouse automation with AI earns its place. It doesn’t just move tasks faster; it reshapes how warehouses function. By finding patterns in data, anticipating bottlenecks & continuously adjusting, AI brings a level of responsiveness that traditional systems simply can’t deliver. The result is not a “futuristic warehouse” but one that finally keeps pace with reality.
Future of AI in Logistics and Warehouse Management
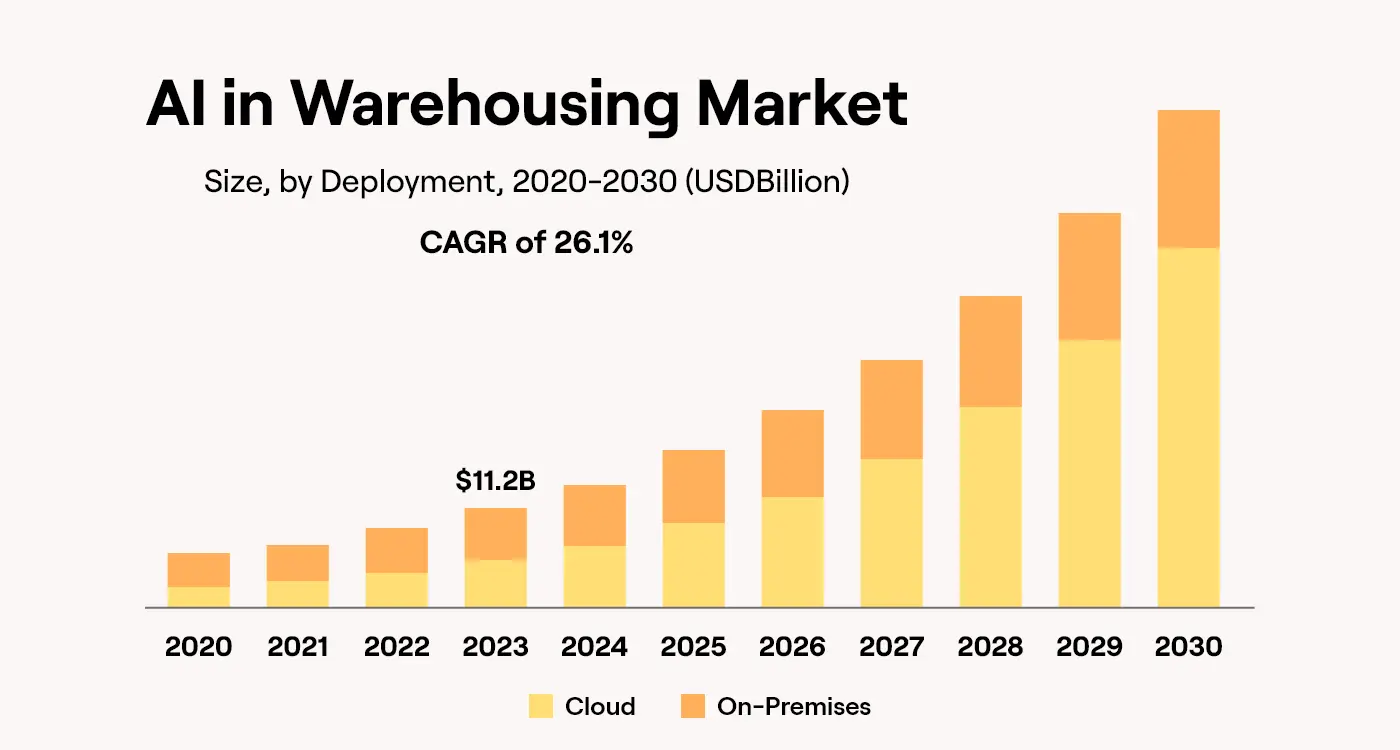
In 2025, warehouses are moving into a new era. They’re not just using smart machines anymore. They are building systems that can learn, adjust & sometimes act on their own.
The big picture- the AI in supply chain market (which includes logistics and warehouses) is growing super fast. Reports show it was about $11.2 billion in 2024 & it could reach more than $35 billion by 2030. Some studies even show it may cross $50 billion by 2031. That means the market is growing by more than 25–35% every year.
What’s happening inside warehouses? Retailers using AI are already seeing big wins-
- 72% of retailers say AI cut their operating costs (NVIDIA survey).
- Companies using AI report lower inventory costs, often by 20–25%.
- They also see faster order processing and better accuracy in shipping.
In short, AI is making warehouses leaner, faster & cheaper to run. And by the early 2030s, experts believe the value of AI in logistics and warehouses will be worth tens of billions of dollars worldwide.
Make Your Warehouse Future-Ready
The numbers are clear- warehouses using AI are cutting inventory costs, improving service levels & delivering faster with fewer errors. The technology is no longer experimental – it’s a practical advantage shaping global supply chains in 2025.
The Evolution of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouses have always been the heart of supply chains. They are where products are stored organized & sent out to customers or stores. But the way warehouses are managed has changed a lot over the years. What started as people using paper lists and clipboards has now turned into smart systems powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI). Let’s take a closer look at how warehouse management evolved step by step.
- From Manual Management to Machines
In the beginning, warehouse work was completely manual. Workers had to remember where each product was placed, write things down on paper & count items by hand. Managers used notebooks and clipboards to track what came in and what went out. Mistakes were common. Sometimes items were lost or misplaced & workers spent hours walking around just to find one box. It was slow, tiring & not very accurate.
Then came computers and spreadsheets. These helped a little – managers could now keep digital records instead of paper files. But even then, most work still depended on people typing information correctly and keeping it updated.
- The Rise of Barcode Systems
The 1980s and 1990s brought a big change – barcode technology. Barcodes are those black-and-white lines you see on packages. When scanned, they show important details about the product, like its name, quantity & location. This made warehouse work faster and more accurate.
Workers could now scan products instead of writing things down & managers could track inventory more easily. It was a big step forward – errors dropped & order processing became quicker. But there was still a problem- barcodes could only tell you where an item was when it was scanned. They didn’t update automatically or show what was happening in real time.
- The Digital WMS Revolution
As technology advanced, companies began using Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) – software that could track inventory, monitor stock levels & manage orders in one place. These systems were connected to barcode scanners and computers, allowing better coordination.
Managers could now see how much stock was available, which orders were pending & how products were moving inside the warehouse. Digital WMS also helped with planning – it suggested which shelves to use or which routes were fastest for picking orders.
However, traditional WMS still had limits. It was mostly reactive – meaning it told you what happened after something went wrong. For example, it could tell you a product was out of stock, but not predict that it would run out soon. It relied heavily on human data entry & when data was wrong or delayed, decisions suffered.
- The Gaps in Traditional WMS
Even with digital systems, warehouses struggled with three big problems-
- Reactive Operations – Traditional WMS could only respond to issues, not prevent them. Managers knew about delays or shortages only after they happened.
- Data Silos – Many warehouses used different systems for orders, shipping & inventory that didn’t “talk” to each other. This made it hard to see the full picture.
- Human Dependency – WMS still depended on workers to scan, upload & update data. If people made mistakes or forgot, the whole system could fail.
These gaps meant that even the most advanced warehouses weren’t truly “smart.” They were faster than before, but not intelligent enough to make predictions or decisions on their own.
- The AI-Powered Warehouse Era
Then came the next big leap – Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI took warehouse management to a whole new level by teaching systems to think and learn from data. Instead of waiting for problems, AI predicts them. Instead of humans tracking every detail, AI does it automatically.
With AI, warehouses no longer just store data – they analyze it. For example-
- AI studies past sales and helps forecast future demand.
- It looks at delivery patterns and suggests the best time to reorder products.
- It even helps design better warehouse layouts by studying how items move in and out.
AI doesn’t work alone – it connects with other smart technologies like IoT (Internet of Things), robotics & ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems.
- IoT sensors send real-time data about temperature, stock levels & machine health.
- Robots powered by AI move products from one place to another quickly and safely.
- ERP systems ensure that warehouse data connects with sales, accounting & supply chain systems.
All these systems work together like parts of one big brain, helping warehouses run faster, safer & smarter.
- From Reactive to Predictive
The biggest change AI brings is the shift from reactive to predictive management. Instead of fixing mistakes after they happen, AI applications helps avoid them altogether. It warns managers before a stock out, tells workers where bottlenecks might occur & suggests the best way to use space or schedule shifts.
AI doesn’t just automate tasks – it helps people make better choices. Workers spend less time fixing problems and more time improving processes.
Also Read: Top 6 Problems Artificial Intelligence Solves in Transportation and Logistics Industry
Benefits of AI in Warehouse Management
In warehouses deploying artificial intelligence is now easier to manage than you might think. Work becomes faster, safer & more precise. And by rooting out problems early rather than fixing them at the last minute, AI is a tool to help prevent accidents. AI is playing a crucial role in warehouse operations – here’s how
- Better Inventory Tracking
AI monitors everything in the warehouse with help from smart sensors and cameras. It knows where each item is, how much of it is remaining & when something needs to be re-ordered. That’s no more guessing or wasting time trying to find those missing things. Store managers can get live updates on a computer or tablet and can better fill customer orders promptly and accurately. - Smarter Demand Forecasting
AI looks at past sales, busy seasons, holidays & even weather changes to predict what products customers will want next. This helps warehouses order the right amount of stock – not too much and not too little. It prevents running out of popular items or filling shelves with products that don’t sell. As a result, the warehouse saves money and space while keeping customers happy. - Faster Picking and Packing
AI enables robots and smart machines to zip through the warehouse to pick and pack orders fast. “These machines are savvy about how to churn products out as quickly as possible, and they make fewer mistakes. This frees workers up to pay attention to still-crucial tasks requiring human dexterity, like verifying quality checks or processing special orders. - Improved Warehouse Layouts
AI observes which products move in and out of the warehouse so that it can propose better ways to organize them. It can suggest where to put fast-selling products for easy access or how shelves might be rearranged to save walking time. This more intelligent arrangement makes it easier to get work done and uses space optimally without the addition of new storage spaces being constructed. - Better Safety
Warehouses can be risky places with heavy boxes, forklifts & busy workers. AI-powered cameras and sensors can spot danger early – like boxes stacked too high or a forklift getting too close to someone. It sends warnings before accidents happen. AI can also remind teams when machines need check-ups, keeping everyone safe and equipment in good shape. - Quicker Decisions
AI helps managers make decisions faster by showing real-time data and suggestions. It can alert them when stock is running low, when to plan shifts or which orders to ship first. Instead of spending hours studying reports, managers can take action immediately. This keeps the warehouse running smoothly and avoids delays.
The best part? Warehouses no longer run in panic mode. They work smoothly, with fewer mistakes, lower costs & faster deliveries for customers – all because of smart AI systems.
The Role of AI in Smart Warehouse Automation
AI in a warehouse is just like the control tower of an airport. The tower does not fly the planes but it ensure that every plane takes off & lands safely at the airport. In the same way, AI doesn’t move boxes itself but it keeps everything in the warehouse running smoothly & safely.
Here’s how the role of AI in smart warehouse automation plays out-
- Sensors everywhere – Tiny sensors on shelves, packages or forklifts send signals about weight, movement or location. AI collects this and creates a live digital map of the warehouse.
- Smart cameras – Instead of people checking every box, AI-powered cameras scan items, read labels & even find damaged goods in seconds. They can also warn about blocked paths.
- Planning work better – AI studies how tasks are done. If a busy week is coming, it suggests hiring extra workers. If one shift has too much work, it helps spread the load.
- Robots and drones – Robots pick items, carry them & pack them. Drones fly up high to check stock in places that are unsafe for people.
- Smarter product placement – AI checks which products sell most and suggests keeping them closer to packing stations. This saves time and helps ship orders faster.
- Saving energy and money – AI watches electricity use, adjusts lights and cooling & cuts waste. These changes save money every day.
In smart warehouses, AI doesn’t replace people-it works with them. Humans bring skills and decision-making, while AI handles heavy data and risky jobs. Together, they create warehouses that don’t just work, but get better every single day.
Cost of Implementing AI in Warehouse Management
Putting AI solutions in a warehouse is not like plugging in a new machine and walking away. It needs planning, setup & training. And yes-it costs money. But here’s the good part-while the starting cost may look big, AI often pays for itself by saving money later.
Here are the main things that decide the cost-
- Hardware – Robots, drones, cameras & sensors. These help AI “see” and “move” around the warehouse.
- Software – AI programs and warehouse management systems that connect everything together. Many run in the cloud, which means monthly or yearly fees.
- Old system connection – Most warehouses already use older software or ERPs. Joining AI with these systems takes extra time and money.
- Training – Workers need to learn how to use AI tools. Good training makes sure people actually use the tools well.
- Maintenance – AI is not “set and forget.” It needs updates, bug fixes & care to keep working smoothly.
- Size of the warehouse – Bigger warehouses cost more to upgrade since they need more devices, storage & automation.
So, how much does it cost?
- Small warehouses may spend tens of thousands of dollars.
- Large warehouses can spend millions.
The good news-many companies get their money back in a few years because AI helps with faster orders, fewer mistakes & lower labor costs.
Cost Breakdown of AI in Warehouse Management
The real value isn’t just in the upfront spend-it’s in what warehouses save later-fewer errors, faster deliveries & smoother workflows that cut operating costs month after month.
| Cost Factor | What It Covers | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Robots, drones, sensors, cameras, IoT devices | $20,000 – $500,000+ |
| Software | AI platforms, WMS, cloud subscriptions | $10,000 – $200,000 annually |
| Integration & Customization | Connecting AI to existing ERP/WMS, custom development | $15,000 – $250,000 |
| Training | Teaching staff to use AI systems, onboarding new processes | $5,000 – $50,000 |
| Maintenance & Support | System updates, bug fixes, AI model retraining | $10,000 – $100,000 yearly |
| Warehouse Size Impact | Larger facilities = more devices, more software licenses | Costs scale with size |
How to Implement AI in Warehouses?
Adopting AI in warehouse management isn’t about plugging in new software – it’s a strategic transformation that reshapes workflows, data handling & decision-making. For warehouse operators, logistics heads or supply chain leaders, the key to success lies in moving from experimentation to measurable efficiency. Below is a step-by-step roadmap that helps warehouses transition from manual processes to fully AI-optimized ecosystems – without disrupting ongoing operations.
Step 1: Assessment and Goal Setting – Identify the Right Problem Areas
Every successful AI journey starts with a clear understanding of where you stand. Begin by assessing your existing warehouse operations – from inventory tracking to labor scheduling – and identify the pain points that most impact costs, speed or customer satisfaction.
Ask yourself:
- Are your stock levels consistently inaccurate?
- Is there excessive downtime due to equipment failure?
- Do pickers spend too much time searching for items?
- Is order fulfillment speed lagging behind competitors?
Once you identify the core problems, set clear, quantifiable goals. For instance:
- “Reduce picking time by 30% within six months.”
- “Cut stock discrepancies by half by the next quarter.”
- “Automate 50% of order scheduling by year-end.”
These KPIs will not only guide your AI implementation but also serve as benchmarks to measure ROI.
It’s also crucial to conduct a data readiness audit-assessing how clean, structured & integrated your warehouse data currently is. Poor-quality or fragmented data can derail even the most sophisticated AI system.
Step 2: Data Collection and Integration – Build the Foundation for Intelligence
AI thrives on data continuity and accessibility. Before you deploy algorithms or predictive tools, ensure your warehouse systems are seamlessly connected.
Most warehouses run on fragmented systems – ERP for finance, WMS for inventory & standalone spreadsheets for dispatch. The challenge lies in breaking these silos and creating a unified data layer that AI can learn from.
Actions to take:
- Integrate existing ERP, WMS & SCM systems into a single platform or data warehouse.
- Connect IoT sensors, barcode scanners & RFID readers to capture real-time activity data.
- Standardize data formats and ensure historical records are digitized.
For instance, when real-time data from scanners, conveyors & GPS systems feeds into an AI engine, it can start identifying inefficiencies – like where stock bottlenecks occur or which routes lead to delays.
Cloud integration tools like AWS IoT, Azure Synapse or Snowflake make this process more scalable and secure.
This stage sets the digital foundation – without it, AI models can’t learn, predict or optimize effectively.
Step 3: Pilot Program and Proof of Concept – Start Small, Learn Fast
Jumping straight into full-scale AI deployment often leads to chaos. The smarter way is to start small with a pilot project or Proof of Concept (PoC). Choose a high-impact, low-risk area such as:
- Demand forecasting for one product category.
- AI-powered pick-path optimization in one zone.
- Predictive maintenance for a single piece of equipment.
A pilot helps you evaluate:
- How AI performs on your real-world data.
- What ROI or process improvements it delivers.
- Where integration or adoption challenges may occur.
During this stage, focus on collecting feedback from warehouse staff and supervisors. Their insights will help fine-tune algorithms, user interfaces & workflows before expansion.
Most successful organizations use agile, iterative testing-gradually refining the system until it aligns with real operational goals.
Once results start showing – like improved accuracy, reduced manual time or lower downtime – use these data points to build an internal business case for broader AI adoption.
Step 4: Full Deployment – Scale AI Across Warehouse Functions
After a successful pilot, move toward full-scale deployment – but do it strategically. Instead of implementing everything at once, roll out AI tools function by function, ensuring continuity and stability.
Key expansion areas include:
- AI-Powered Inventory Tracking: Automated updates using computer vision and RFID.
- Automated Picking & Sorting: Robots guided by AI vision systems and dynamic path algorithms.
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring equipment health in real time.
- Workforce Optimization: Using AI to allocate staff based on workload and skillset.
During deployment, it’s critical to establish data governance policies and cybersecurity protocols. As more devices and sensors come online, so does your exposure to potential breaches.
Also, consider creating a Central AI Command Center – a dashboard where managers can view analytics, receive alerts & make real-time decisions across operations.
A gradual rollout ensures that humans and AI systems coexist effectively – each learning and adapting from the other to create a steady rhythm of performance.
Step 5: Continuous Training and Optimization – Keep AI Learning
AI isn’t a one-time setup; it’s a continuous learner. Once deployed, your models should keep improving as they absorb more data and adapt to changing warehouse dynamics.
Implement a feedback loop where:
- Supervisors validate AI predictions (e.g., reorder recommendations, routing paths).
- System performance is reviewed monthly or quarterly.
- New data is used to retrain and fine-tune models.
Keep your workforce in the loop through continuous training programs that blend technical learning with operational insights.
For example:
- Teach staff how to interpret AI-driven dashboards.
- Empower technicians to use predictive alerts for maintenance.
- Encourage warehouse managers to collaborate with data analysts to refine algorithms.
By maintaining this cycle of training and optimization, warehouses evolve from reactive operations to self-improving ecosystems-where every process gets smarter over time.
Read More: How AI is Effective in Logistic Industry
Best Practices for Smooth Change Management
AI adoption succeeds not because of technology alone but because of how well people embrace it. Change management ensures minimal resistance, maximum adoption & cultural alignment.
Here are key best practices:
- Involve Teams Early: Engage warehouse managers, floor staff & IT teams in discussions before rollout. Early inclusion builds trust.
- Communicate the “Why”: Explain how AI will simplify their jobs – not replace them.
- Train Continuously: Offer structured workshops and on-floor demos to boost confidence.
- Monitor and Celebrate Wins: Share real improvements (e.g., “Picking time reduced by 20% this month”) to motivate teams.
- Ensure Leadership Support: AI transformation needs executive buy-in for funding, visibility & morale.
- Choose the Right Partners: Collaborate with AI solution providers experienced in warehouse automation who understand integration, security & scalability challenges.
Successful adoption is not a sprint but a journey – one that demands patience, planning & collaboration between technology and people.
How AI Transforms Warehouse Operations?
The introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the way modern warehouses function. What once relied on human intuition, paper-based tracking & static workflows has evolved into a dynamic, data-driven ecosystem where every process- from forecasting to fulfillment-operates with precision, speed & intelligence.
AI transforms warehouse operations by connecting people, machines & data into one intelligent network. Through real-time analytics, machine learning & automation, it helps warehouse managers not only respond to operational challenges but also predict and prevent them. Here’s how AI is reshaping each layer of warehouse management.
4.1. Predictive Demand Forecasting
One of the most critical aspects of warehouse success is the ability to forecast demand accurately. Traditional forecasting models rely on past sales data and simple seasonal assumptions. However, today’s supply chains are influenced by multiple dynamic variables-economic shifts, weather changes, social trends & even viral online content.
AI-powered predictive analytics solves this complexity by analyzing diverse data sets such as:
- Historical sales and replenishment cycles
- Regional buying patterns and demographic data
- Weather forecasts and holidays
- Real-time market and pricing data
Using machine learning algorithms, AI identifies hidden correlations and patterns that humans might overlook. For example, an AI model might learn that umbrella demand spikes two weeks before monsoon season in specific regions or that certain promotions drive higher-than-average restocks.
This predictive power helps warehouses balance inventory more intelligently, reducing overstocking (which ties up capital) and understocking (which causes missed sales). Amazon, for instance, uses AI-based forecasting to ensure popular items are stocked in nearby fulfillment centers even before customers order them-a practice that reduces shipping time and boosts satisfaction.
In essence, AI forecasting turns reactive warehouses into proactive ones, enabling strategic planning and seamless coordination across the supply chain.
4.2. Automated Picking and Sorting Robots
Order picking is one of the most labor-intensive and error-prone warehouse processes. Manual picking often results in delays, mispicks & high labor costs. AI-driven robotics addresses this by bringing speed, accuracy & consistency to the process.
Modern warehouses deploy vision-guided robots and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) equipped with AI algorithms that can:
- Navigate complex layouts using pathfinding and obstacle detection
- Identify products using computer vision and barcode recognition
- Optimize picking routes in real-time to reduce travel distance
These robots collaborate with human workers rather than replace them. For example, a robot can bring shelves to a human packer, reducing walking time, while the human focuses on final verification or fragile handling.
Companies like Ocado and DHL use AI-driven robotic arms capable of identifying, grasping & sorting items of various shapes and textures without human assistance. The outcome? Faster picking times (up to 50% improvement), lower labor dependency & nearly zero picking errors.
By merging robotics with AI decision-making, warehouses can sustain 24/7 operations, scale during peak demand & maintain consistent output quality.
4.3. Intelligent Inventory Tracking
Inventory inaccuracies are a silent profit drain for warehouses. A misplaced pallet or miscounted item can ripple through the entire fulfillment chain. AI-enabled inventory tracking eliminates this guesswork by combining computer vision, RFID & IoT sensors.
Every item entering or leaving the warehouse is automatically scanned and tracked in real time. Cameras and AI models identify products, verify labels & detect discrepancies instantly-without requiring manual barcode scanning.
For example, AI-powered drones equipped with image recognition fly through aisles during off-hours, capturing data on stock levels, shelf positions & empty bins. The AI system processes this data and updates the warehouse management system (WMS) instantly.
Additionally, smart alerts notify managers about damaged goods, misplaced inventory, or potential stockouts before they occur. This real-time visibility improves accuracy rates, reduces shrinkage & helps managers make faster replenishment decisions.
The result is a synchronized, transparent inventory ecosystem where every product is visible from arrival to dispatch-reducing operational stress and boosting customer satisfaction.
4.4. AI-Powered Warehouse Layout Optimization
Space utilization is one of the most undervalued yet critical factors in warehouse productivity. Many facilities waste 10–20% of available space due to static layouts and outdated storage configurations. AI-powered spatial optimization addresses this inefficiency.
Using digital twins and simulation modeling, AI creates a virtual replica of the warehouse to test different layout scenarios. It then analyzes how goods move, how often items are picked & where congestion occurs to suggest an optimal setup.
For example, AI might recommend placing fast-moving products closer to packing stations or redesigning aisles to minimize forklift travel time. Over time, as order trends evolve, the AI continuously learns and adjusts the layout suggestions.
This adaptability ensures that warehouses don’t just run efficiently once-but remain efficient year after year. By applying spatial intelligence, companies can increase usable space by up to 30% and improve worker productivity without physical expansion.
4.5. Predictive Maintenance
Every minute of equipment downtime costs money. Forklifts, conveyor belts, scanners & robotic arms are the backbone of warehouse operations & unplanned breakdowns can halt entire workflows.
AI-driven predictive maintenance uses machine learning algorithms to analyze sensor data from these machines-temperature, vibration, energy consumption & operational patterns-to detect early signs of wear or malfunction.
Instead of reactive servicing (fixing something after it breaks), predictive models forecast when a part will likely fail and alert maintenance teams in advance.
For instance, if an AI model detects an abnormal vibration pattern in a conveyor motor, it can schedule a repair before the issue causes a breakdown. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, extends equipment lifespan & saves thousands in repair costs.
Predictive maintenance transforms maintenance from a cost center into a strategic advantage-keeping operations smooth and uninterrupted.
4.6. Safety Monitoring with Computer Vision
Warehouses are high-risk environments with heavy machinery, forklifts & human traffic operating side by side. Even a minor lapse can lead to accidents. AI, particularly computer vision, now acts as an ever-watchful safety supervisor.
AI-powered cameras monitor live video feeds to detect unsafe actions-such as workers entering restricted zones, forklifts moving too close to pedestrians, or boxes stacked beyond safe height limits.
If a potential hazard is detected, AI instantly triggers alerts through visual signals or mobile notifications, allowing safety teams to intervene before accidents occur.
Some systems even track worker posture to identify fatigue or improper lifting techniques, helping prevent long-term injuries.
These real-time safety insights not only protect employees but also ensure compliance with OSHA and ISO safety regulations. The result is a safer, more confident workforce and a dramatic reduction in accident-related downtime.
4.7. Route Optimization & Autonomous Vehicles
In large warehouses, even a few seconds saved per trip can translate into massive time and cost savings. AI-driven route optimization algorithms help plan and direct the most efficient paths for forklifts, AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) & AMRs.
By analyzing traffic patterns, shelf positions & order priorities, AI determines the shortest and safest routes for each vehicle. When conditions change-say, an aisle becomes congested or blocked-the system recalculates paths in real-time.
For example, autonomous forklifts use LiDAR sensors and computer vision to navigate smoothly, avoiding collisions and optimizing fuel or battery use. Drones can also deliver lightweight items to packing stations in seconds, reducing manual walking time.
Through these smart routing systems, warehouses experience up to 35% faster internal movement, improved fuel efficiency & fewer accidents.
In short, AI ensures that every vehicle, robot & worker moves with purpose-no wasted time, no unnecessary detours.
Read More: How to Build a Logistics and Transportation App Like Aramex?
4.8. Real-time Decision Intelligence Dashboards
Data without interpretation is just noise. AI transforms raw warehouse data into real-time, actionable insights through intelligent dashboards that provide a 360° operational view.
Warehouse managers can monitor KPIs such as order accuracy, equipment health, space usage, labor productivity & energy consumption-all in one place.
If an issue arises-say, delayed orders or low stock-AI automatically identifies the root cause and recommends corrective actions. For example, it might detect that order delays are caused by bottlenecks in picking zones and suggest redistributing staff or altering workflows.
Some advanced systems even simulate “what-if” scenarios to help decision-makers predict outcomes before implementing changes.
The combination of predictive analytics and prescriptive intelligence empowers managers to act faster, make better decisions & continuously optimize warehouse performance.
Key Challenges in Warehouse Management
Running a warehouse involves many moving parts and constant coordination between people, equipment & systems. Even small errors can cause delays, losses or customer dissatisfaction. Below are some of the key challenge’s warehouses face today, explained in simple terms-
- Inventory Mistakes
One of the most common issues in warehouse management is incorrect inventory data. This happens when stock levels recorded in the system do not match the actual goods on the shelves. It leads to problems such as overselling, stockouts & wasted time searching for missing items. When the inventory count is unreliable, customer orders get delayed and overall efficiency decreases. - Not Enough Workers
Warehousing requires physical effort and long working hours. Many workers find these jobs tiring & it has become increasingly difficult to recruit and retain staff. As demand for online shopping grows, labor shortages make it hard for warehouses to keep up with order volumes. Rising wages and high employee turnover also increase operational costs for companies. - Fast Changes in Demand
Customer demand often fluctuates due to seasonal trends, holidays or market conditions. Traditional warehouse systems are not designed to handle sudden spikes or drops in orders. When demand rises quickly, warehouses may struggle to fulfill all requests on time. When it drops, excess inventory occupies valuable storage space and ties up capital. - Safety Risks
Warehouses involve constant movement of heavy goods, forklifts & machinery. Without strict safety standards and regular maintenance, the risk of accidents, injuries & equipment damage increases. Unsafe conditions not only endanger workers but also cause costly disruptions in operations and potential legal consequences for the company. - Wasted Space
Inefficient use of space is another major problem. Some storage areas remain empty while others are overcrowded. Poor layout planning or incorrect product placement can make it harder for workers to move around and locate items quickly. This limits the total storage capacity and reduces the speed of order processing. - Disconnected Systems
Many warehouses still use outdated software or systems that do not integrate with newer technologies. When information is stored in different platforms that do not communicate with each other, it becomes difficult to track real-time data such as inventory levels order status or shipment details. This lack of visibility slows decision-making and increases the chances of costly mistakes.
Together, these challenges create inefficiencies that raise costs, slow operations & reduce customer satisfaction. To overcome them, many warehouses are now adopting AI-driven solutions that improve accuracy, streamline processes & create safer, more connected environments.
Wrapping Up
Warehouses used to run on checklists and manual systems. That worked when orders were slower. Today, it doesn’t. The pace of e-commerce, rising costs & higher customer expectations have made the old way unsustainable.
That’s why more companies are turning to AI in warehouse management. The benefits are measurable. Inventory errors drop. Forecasting gets sharper. Deliveries move faster. Workers stay safer. And costs go down. In fact, reports from 2025 show that businesses using artificial intelligence in warehouse operations cut inventory costs by up to 35% and improved service levels by more than 60%.
The future of AI in logistics and warehouse management is heading toward smart warehouse solutions where humans and machines share the workload. AI doesn’t replace people; it helps them focus on higher-value work while automation handles the repetitive tasks.
If you’re in logistics or retail, waiting has a cost. Competitors are already building efficiency with the role of AI in smart warehouse automation. The question isn’t if you should invest. It’s when. The earlier you start, the faster you see results.
Turn Warehouse Bottlenecks into Growth Opportunities
Struggling with inventory errors or slow deliveries? See how AI can change your results.
Frequently Asked Questions
For a mid-sized operation, costs can start around $50000 for software and sensors & go up to $500,000+ if robotics are added. The range depends on how automated you want to go.
In most cases, AI tools are designed to plug into your current system. Full replacement is rarely needed unless the old system is very outdated.
Many warehouses report ROI within 18 to 24 months. Savings usually come from fewer errors, faster order processing & reduced labor costs.
Small warehouses benefit too – especially with AI-driven inventory tracking and demand forecasting. Even modest improvements in accuracy can save thousands each year.
It’s not the tech – it’s training staff. Workers need time to adapt to new systems. Companies that invest in clear training usually see smoother adoption and faster results.
Featured Blogs
Read our thoughts and insights on the latest tech and business trends
List of Top AI Agent Development Companies in the USA (2026 Guide)
- March 5, 2026
- AI Agent
In a Nutshell AI agents are the next evolution of automation, going beyond chatbots to perform real business tasks. They can understand intent, connect with tools, and execute multi-step workflows across teams. Businesses are increasingly... Read more
Hire Custom Software Developers in UAE for Secure and Scalable Enterprise Solutions
- February 27, 2026
- Digital Transformation Staff Augmentation
In a Nutshell UAE enterprises are shifting toward custom software because off-the-shelf tools fail to meet complex workflows and regional compliance needs. Custom enterprise software includes ERP modernization, automation systems, secure portals, analytics dashboards, and... Read more
Top 20+ PHP Development Companies in United States (2026)
- February 24, 2026
- Web Development
PHP is one of the most reliable and popular programming languages in the world used for developing dynamic, customizable, secure and affordable web applications. In 2026, SaaS, eCommerce, healthcare, fintech and logistics companies along with Enterprise... Read more





